08 Jun D-layer
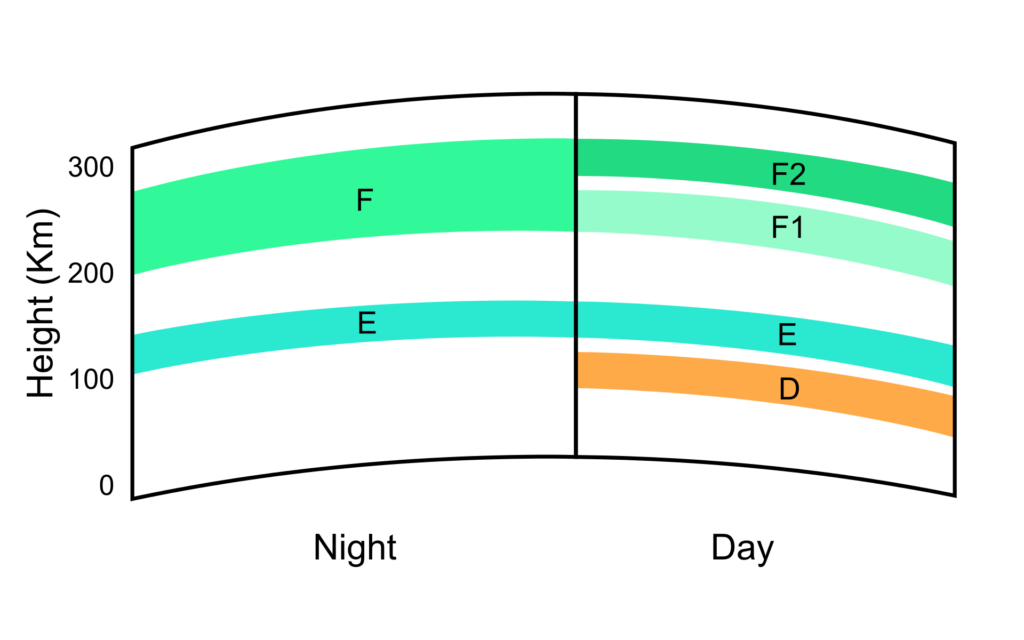
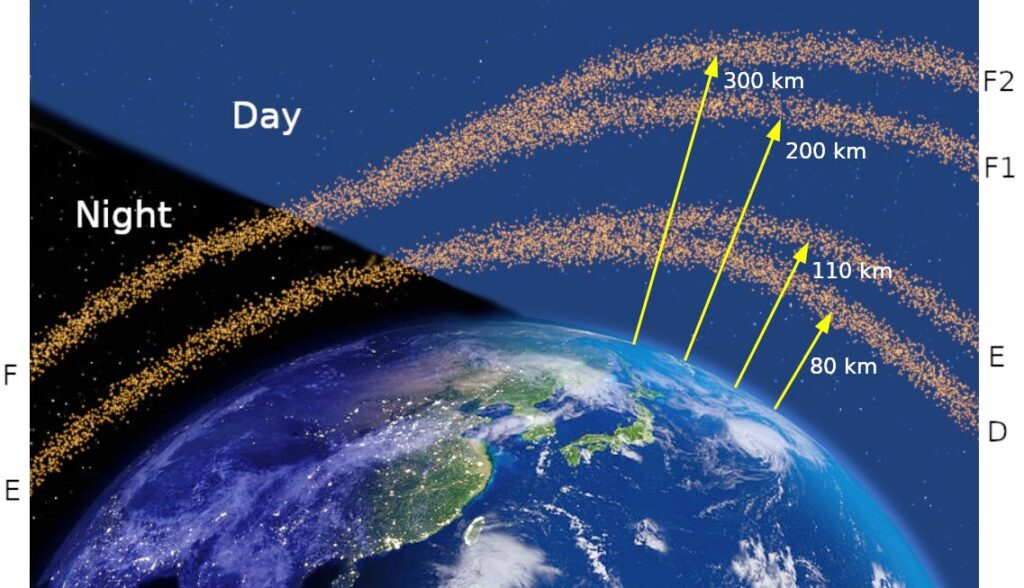
The D layer is the innermost layer, 48 to 90 km (30 to 56 mi) above the surface of the Earth.
Medium frequency (MF) and lower high frequency (HF) radio waves are significantly attenuated within the D layer, as the passing radio waves cause electrons to move, which then collide with the neutral molecules, giving up their energy. Lower frequencies experience greater absorption because they move the electrons farther, leading to a greater chance of collisions. This is the main reason for the absorption of HF radio waves, particularly at 10 MHz and below, with progressively less absorption at higher frequencies. This effect peaks around noon and is reduced at night due to a decrease in the D layer’s thickness; only a small part remains due to cosmic rays. A common example of the D layer in action is the disappearance of distant AM broadcast band stations in the daytime.
During solar proton events, ionization can reach unusually high levels in the D-region over high and polar latitudes. Such very rare events are known as Polar Cap Absorption (or PCA) events because the increased ionization significantly enhances the absorption of radio signals passing through the region. In fact, absorption levels can increase by many tens of dB during intense events, which is enough to absorb most (if not all) transpolar HF radio signal transmissions. Such events typically last less than 24 to 48 hours.
« Back to Glossary Index